Graph Databases - Why?
###Graph Databases
“Graph analysis is possibly the single most effective competitive differentiator for organizations pursuing data driven operations and decisions after the design of data capture.” Gartner Research
####Why Does it actually matter ?
#####Data Size
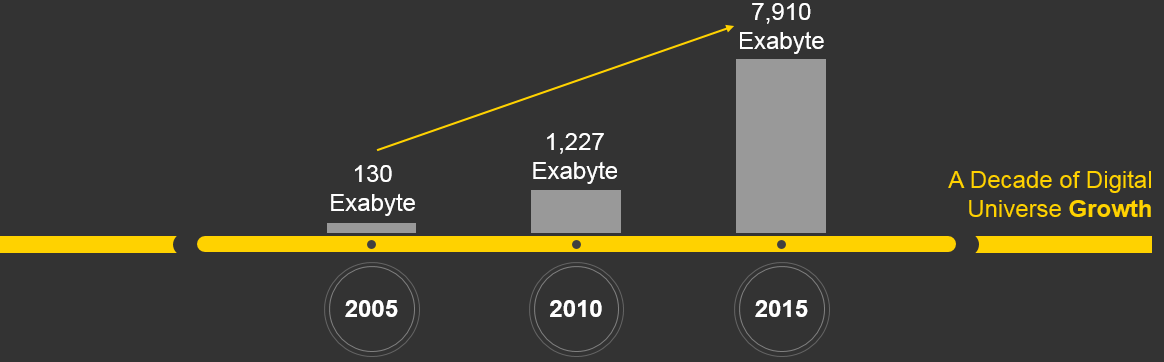
Exabyte’s of data stored per year — the IDC Digital Universe study projects enormous growth in the amount of data being created and stored each year
#####Connectedness
Over time data has evolved to be more and more interlinked and connected
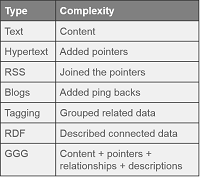
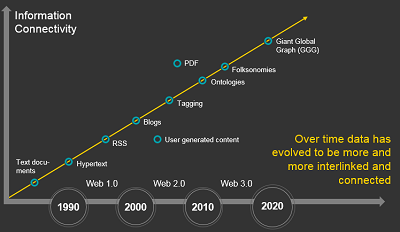
#####Semi-Structure
Accelerated by the decentralization of content generation that is the hallmark of the age of participation (“Web 2.0”)
-
Individualization of content In the salary lists of the 1970s, all elements had exactly one job In the salary lists of the 2000s, we need 5 job columns! Or 8? Or 15? If you tried to collect all the data of every movie ever made, model will have Actors, Characters, Locations, Dates, Costs, Ratings, Showings, Ticket Sales, etc.
-
Architectural Changes Moving towards decoupled services with their own backend by the 2000s
#####Performance
We are building applications today that have complexity requirements that a Relational Database cannot handle with sufficient performance
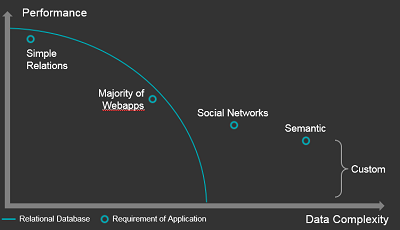
Challenges Faced by todays Enterprise
- Fundamental challenge — there’s far more data than what can be handled
- The big data tidal wave that is transforming the database management industry, employee skill sets, and business strategy
- Identifying solutions that are key to discovering, capturing, and making sense of complex interdependences and relationships, both for running an IT organization more effectively and for building next-generation functionality for businesses
- How to model and navigate networks of data, with extremely high performance The rise of sensors and connected devices leading to variety and velocity of data
Why Graphs
Graphs are Everywhere - The real world, unlike the forms-based model behind the relational database, is rich and interrelated, uniform and rule-bound in parts, exceptional and irregular in others.Graphs are extremely useful in understanding a wide diversity of datasets in fields such as science, government, and business.Gartner identifies five graphs in the world of business — social, intent, consumption, interest, and mobile.The ability to leverage graphs provides a “sustainable competitive advantage” (Gartner).
Graph Databases
NoSQL databases can be categorized according to their data model into the following four categories:
- Key-Value-stores
- BigTable-implementations
- Document-stores
- Graph Databases
A graph database management system (a graph database) is an online database management system with Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) methods that expose a graph data model.Graph databases are generally built for use with transactional (OLTP) systems.They are normally optimized for transactional performance, and are engineered with transactional integrity and operational availability. Relationships are first-class citizens of the graph data model.No complexity like other database management systems which require us to infer connections between entities using contrived properties such as foreign keys, or out-of-band processing like map-reduce.By assembling the simple abstractions of nodes and relationships into connected structures, graph databases enable us to build arbitrarily sophisticated models that map closely to our problem domain.The resulting models are simpler and at the same time more expressive than those produced using traditional relational databases and the other NOSQL stores
Key Features
- Schema Less and Efficient storage of Semi Structured Information
- No O/R (Object/Relational) mismatch — very natural to map a graph to an Object Oriented language like Ruby
- Express Queries as Traversals - Fast deep traversal instead of slow SQL queries that span many table joins
- Very natural to express graph related problem with traversals (recommendation engine, find shortest path etc.)
- Seamless integration with various existing programming languages
- ACID Transaction with rollbacks support
- Whiteboard friendly — you use the language of node, properties and relationship to describe your domain (instead of, e.g., UML) and there is no need to have a complicated O/R mapping tool to implement it in your database
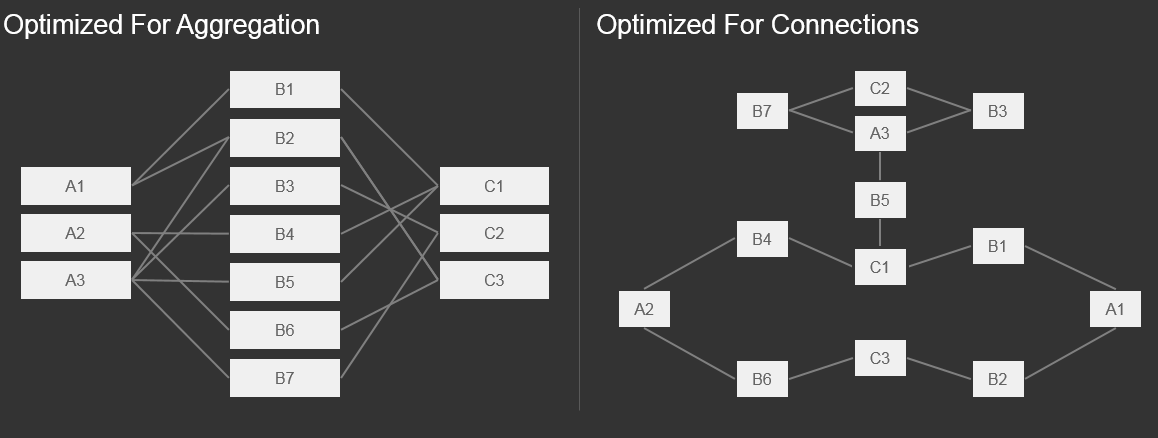
Optimized For Connections vs Aggregations in RDBMS
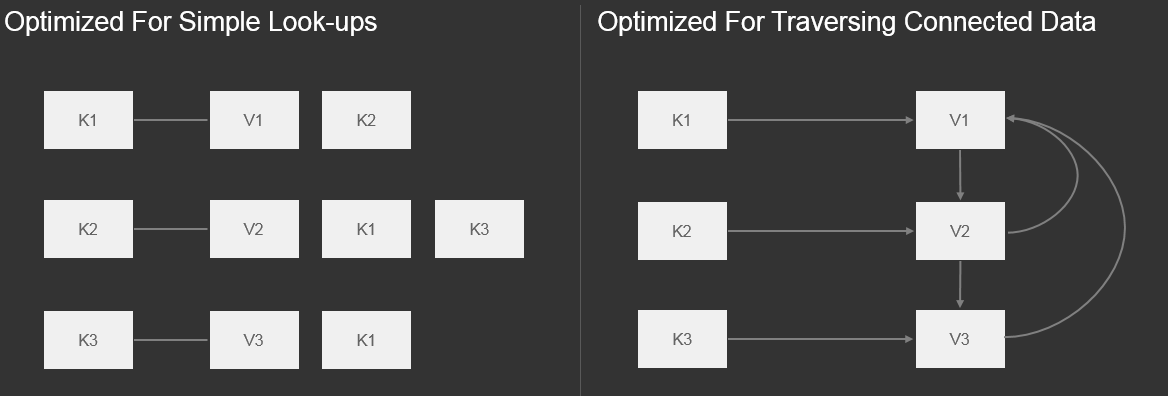
Optimized For Traversing Connected Data vs Simple Look-ups in Key-Value Stores
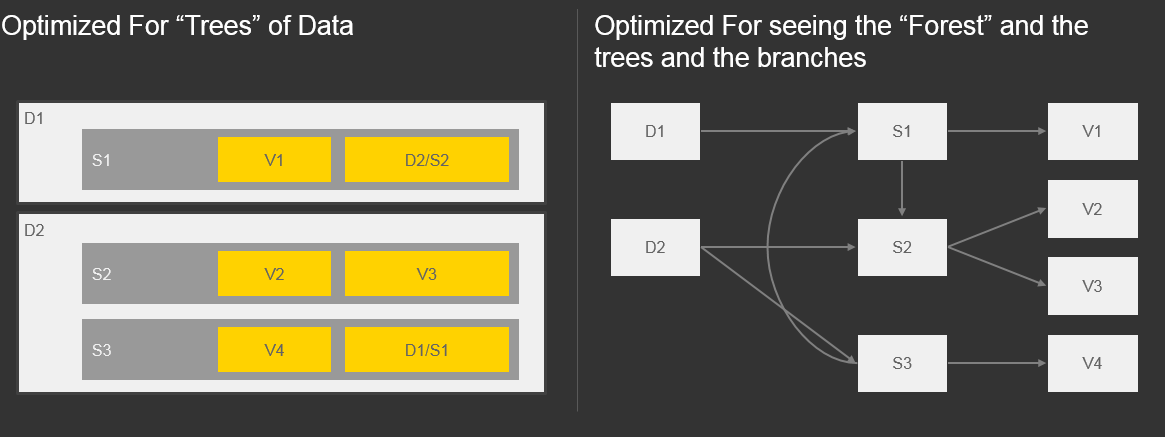
Optimized For seeing the “Forest” and the trees and the branches vs “Trees” of Data
Performance
Sheer performance increase when dealing with connected data versus relational databases and NOSQL stores.In relational databases, where join-intensive query performance deteriorates as the dataset gets bigger, with a graph database performance tends to remain relatively constant, even as the dataset grows.
Flexibility
The graph data model expresses and accommodates business needs in a way that enables IT to move at the speed of business.Graphs are naturally additive - we can add new kinds of relationships, new nodes, new labels, and new subgraphs to an existing structure without disturbing existing queries and application functionality.Fewer migrations, thereby reducing maintenance overhead and risk.
Agility
- Easy to evolve the data model in step with the rest of our application
- Equip us to perform frictionless development and graceful systems maintenance thereby empowering us to evolve an application in a controlled manner
- Being schema free, graph databases lack the kind of schema-oriented data governance mechanisms as in relation databases but they provide a far more visible and actionable kind of governance.Governance is typically applied in a programmatic fashion, using tests to drive out the data model and queries, as well as assert the business rules that depend upon the graph.Provides a agile and test-driven software development practices, allowing graph database — backed applications to evolve in step with changing business environments.
Why Organizations Choose Graph Databases
-
“Minutes to milliseconds” performance: Query performance and responsiveness are top of many organizations’ concerns with regard to their data platforms.
- Drastically accelerated development cycles:
The graph data model reduces:
- Impedance mismatch by reducing the development overhead of translating back and forth between an object model and a tabular relational model
- Mismatch between the technical and business domains: Subject matter experts, architects, and developers can talk about and picture the core domain using a shared model that is then incorporated into the application itself
-
Extreme business responsiveness The schema-free nature of a graph database coupled with the ability to simultaneously relate data elements allows a graph database solution to evolve as the business evolves, reducing risk and time-to-market.
- Enterprise ready Data is important: When employed in a business-critical application, a data technology must be robust, scalable, and more often than not, transactional Matured graph databases available provide all the —ilities:ACID (Atomic, Consistent, Isolated, Durable), Transactionality,High-availability,Horizontal read scalability, Performance and flexibility, Storage of billions of entities — needed by large enterprises
The Graph Database Space
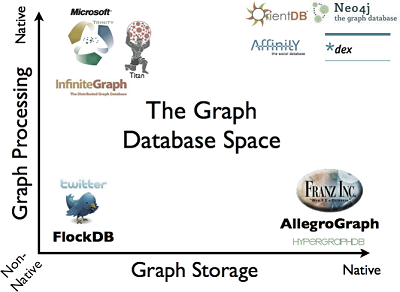
“Over 25 percent of enterprises will use graph databases by 2017.” Forrester Research
References
Neo4j Neotechnology Graphaware Neo4j Developer Infoq Slideshare Forbes Gartner